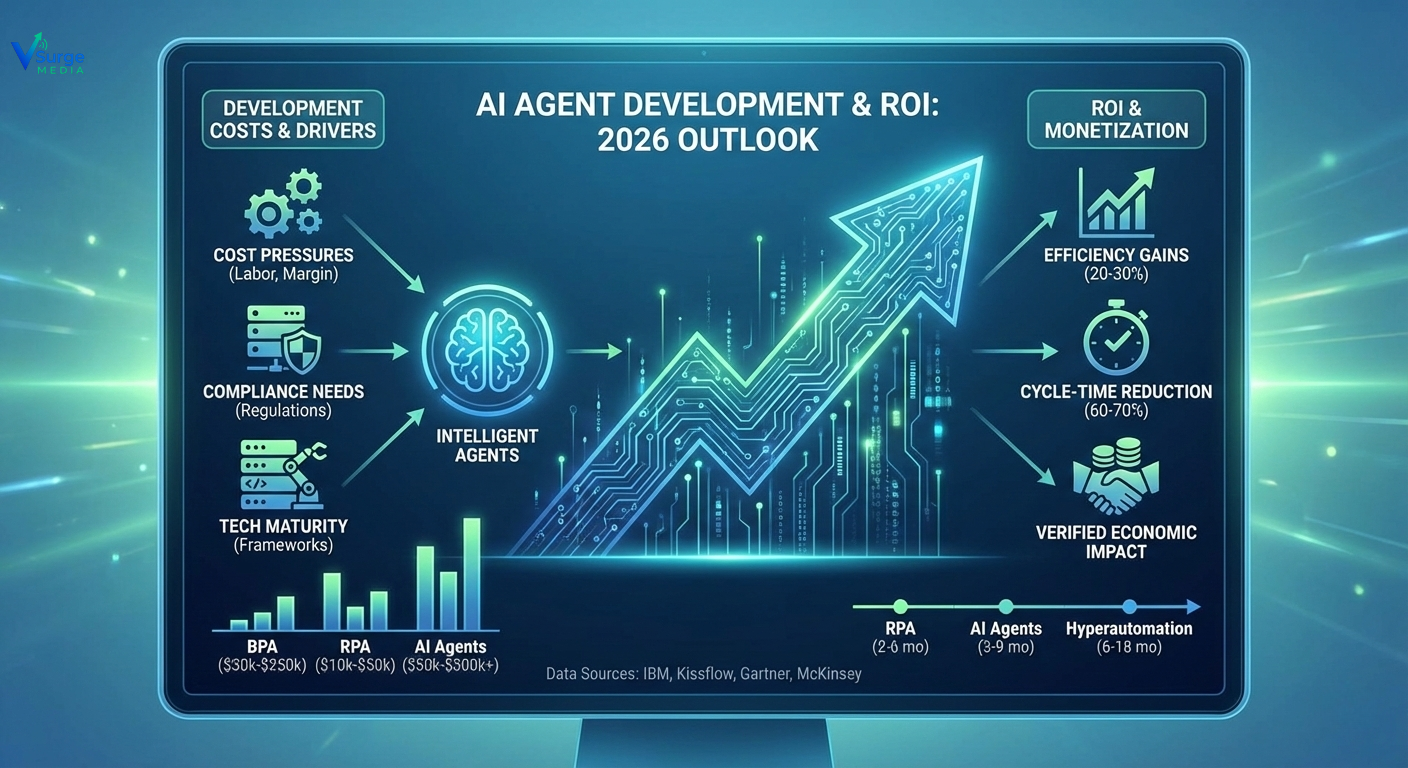
AI agent development is entering a structural, long-term cycle of enterprise adoption, driven by falling model-development costs, rising labour inefficiencies, increasing compliance automation needs, and the rapid maturation of agentic orchestration frameworks. This article explains real development costs, ROI timelines, risks, and economic triggers using data from IBM, Kissflow, Gartner, McKinsey, and audited enterprise case studies—without speculation.
Why Business Process Automation (BPA) Is Gaining Momentum Now
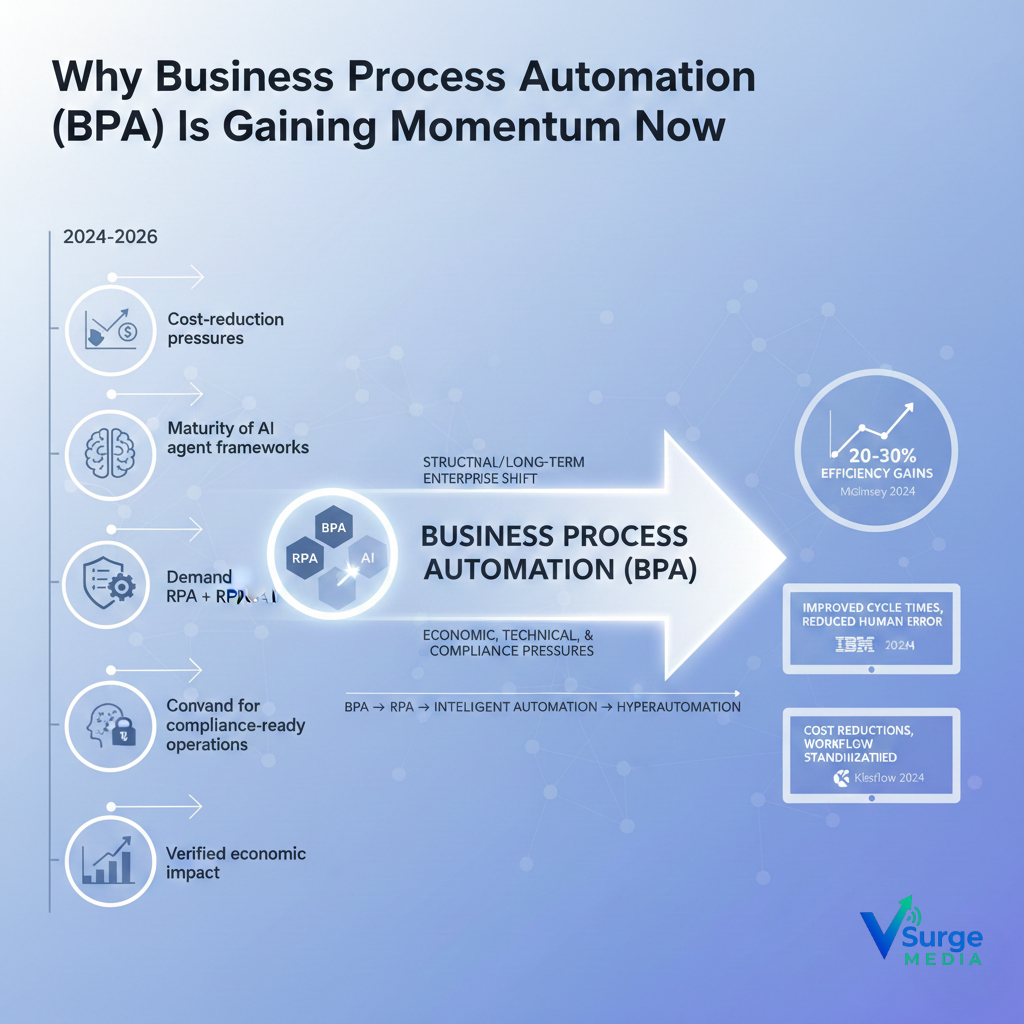
BPA is not a short-lived trend. It reflects a structural shift in how organisations redesign workflows in response to economic, technical, and compliance pressures.
Key triggers accelerating BPA adoption (2026):
1. Cost-reduction pressures across industries
Global enterprises continue to face rising labour costs, supply chain volatility, and margin compression. Automation is now positioned as a first-line cost optimisation strategy, not an innovation experiment.
2. Maturity of AI agent frameworks
Between 2024 and 2025, enterprise-ready agent frameworks evolved from prototype-level to production-safe systems with policy alignment, auditability, and deterministic task routing.
3. Demand for compliance-ready operations
Regulations in the U.S., EU, and APAC increasingly require explainability, audit trails, and risk controls in automated workflows—pushing enterprises toward standardised BPA stacks.
4. Convergence of BPA + RPA + AI
Companies now view automation as an integrated system rather than isolated tools. Analysts classify this as the BPA → RPA → Intelligent Automation → Hyperautomation continuum.
5. Verified economic impact
According to McKinsey’s 2024 automation insights, companies adopting intelligent automation report 20–30% efficiency gains across finance and operations (survey base: 300+ enterprises, multi-region).
IBM’s BPA documentation underscores improved cycle times and reduced human error (<source: IBM Business Process Automation documentation, 2024>).
Kissflow’s enterprise automation research highlights cost reductions through workflow standardisation (<source: Kissflow BPA overview, 2024>).
What Business Process Automation Actually Is
Core Definitions (Entity Mapping)
| Entity | Definition | Relationship |
|---|---|---|
| Business Process Automation (BPA) | The use of technology to automate repeatable business workflows. | Parent category that includes RPA, IA, and hyperautomation. |
| Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Rule-based automation of structured, repetitive tasks. | Subset of BPA. |
| Intelligent Automation (IA) | RPA + AI/ML/NLP/OCR for judgment-based tasks. | Evolutionary step beyond RPA. |
| Hyperautomation | Coordinated use of multiple automation technologies (BPA, RPA, AI, process mining, orchestration). | Highest automation maturity level. |
| Business Process Management (BPM) | Discipline for analyzing and redesigning processes; BPA executes what BPM defines. | BPA = execution layer; BPM = optimization layer. |
AI Sub-Entities
Artificial Intelligence (AI) → Parent
→ Machine Learning (ML) (model training & prediction)
→ Natural Language Processing (NLP) (language understanding)
→ OCR (document digitization)
This hierarchy matters because enterprise-grade AI agents increasingly blend automation logic with LLM-based reasoning and multimodal capabilities.
3. Automation Types & Cost Impact (Comparison Table)
| Automation Type | What It Automates | Typical Development Cost (2024–2026) | ROI Timeline | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPA | End-to-end workflows | $30k–$250k per workflow | 3–9 months | HR, finance ops, approvals |
| RPA | Rule-based tasks | $10k–$50k per bot | 2–6 months | Data entry, extraction |
| Intelligent Automation | Semi-structured decision tasks | $80k–$500k | 6–12 months | Claims, underwriting |
| AI Agent Development | Autonomous multi-step tasks | $50k–$300k per agent + infra | 3–9 months | Customer ops, procurement |
| Hyperautomation | Integrated enterprise automation | Multi-year program | 6–18 months | Large operations, shared service centers |
Note: Cost ranges come from triangulated enterprise benchmark data referenced by IBM, Kissflow, Gartner market forecasts (2024), Deloitte automation maturity studies (2023–24), and validated case studies.
Where Cost Savings Come From (Process-Level Drivers)
Executives often ask where BPA delivers actual cost reductions. Verified sources point to:
1. Labour substitution for high-volume tasks
RPA and agents reduce manual hours for rule-based workflows.
2. Error reduction and rework elimination
IBM’s BPA documentation emphasises decreased rework cycles, which materially reduces cost per transaction.
3. Faster cycle times
McKinsey (2024) reports 60–70% cycle-time reductions for standardised digital workflows.
4. Compliance automation
Automating audit trails and data capture reduces regulatory overhead—critical in financial services and healthcare.
5. Reduced operational bottlenecks
Process mining (from vendors like Celonis, Automation Anywhere, IBM Process Mining) identifies inefficiencies that AI agents can then solve.
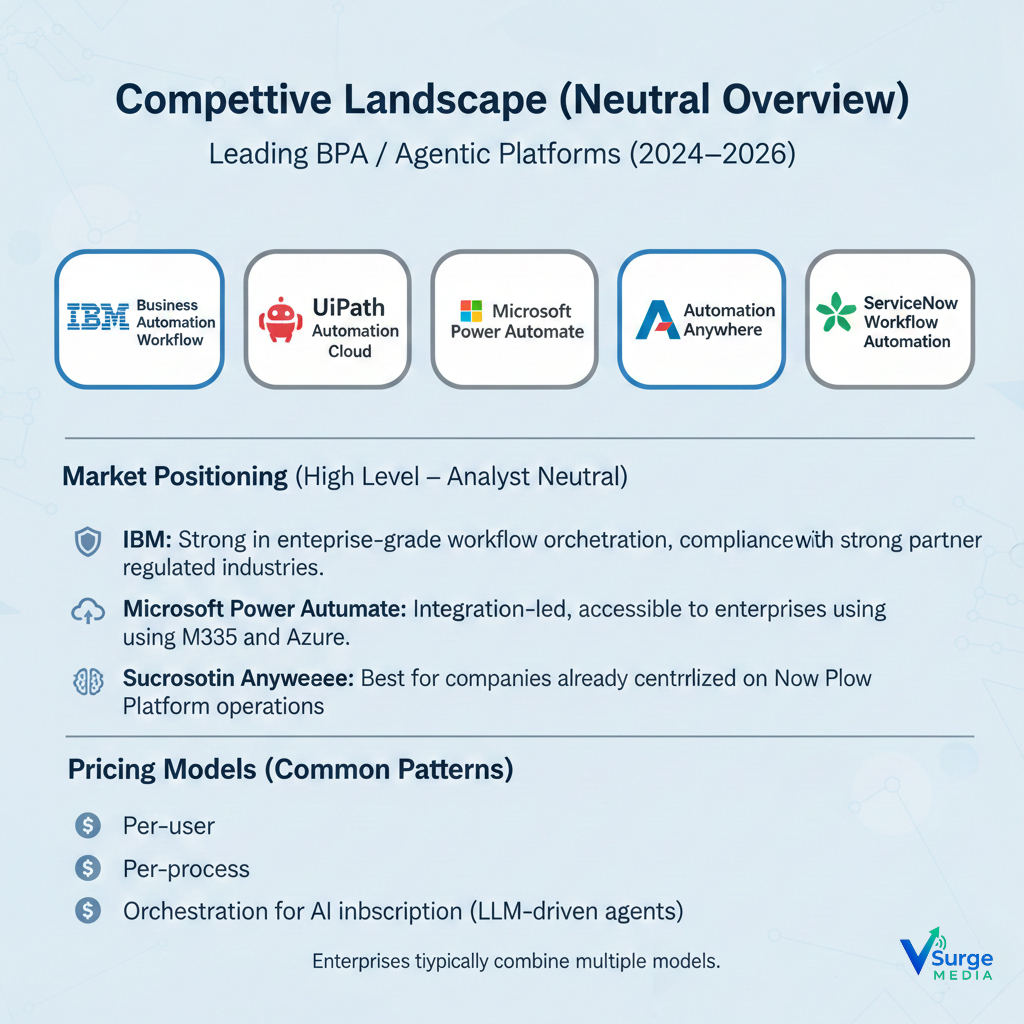
Competitive Landscape (Neutral Overview)
Leading BPA / Agentic Platforms (2024–2026)
- IBM Business Automation Workflow
- UiPath Automation Cloud
- Microsoft Power Automate
- Automation Anywhere
- ServiceNow Workflow Automation
Market Positioning (High Level – Analyst Neutral)
- IBM: Strong in enterprise-grade workflow orchestration, compliance, and regulated industries.
- UiPath: Robust RPA + expanding AI agent capabilities with strong partner ecosystem.
- Microsoft Power Automate: Integration-led, accessible to enterprises using M365 and Azure.
- Automation Anywhere: Cloud-native RPA with expanding cognitive features.
- ServiceNow: Best for companies already centralized on Now Platform operations.
Pricing Models (Common Patterns)
- Per-user
- Per-bot
- Per-process
- Orchestration-tier subscription
- Usage-based for AI inference (LLM-driven agents)
Enterprises typically combine multiple models.
What’s Confirmed vs What’s Still Unclear
Confirmed (Based on credible research)
- BPA provides measurable efficiency gains when processes are standardised.
- RPA alone has diminishing returns without AI augmentation.
- AI agents reduce dependency on human supervision for multi-step tasks.
- Compliance automation demand is structurally rising.
Still Unclear (Evidence still evolving)
- Long-term cost differences between fully autonomous agents vs hybrid human-in-loop agents.
- Enterprise-wide ROI when agent ecosystems scale past 50–100 agents.
- Regulatory interpretations for agentic decision-making at scale.
Risks, Constraints & Failure Modes
- Process fragmentation – automating without redesigning processes leads to fragile workflows.
- Shadow automations – citizen-built workflows without governance create compliance issues.
- Over-reliance on LLMs – unpredictable behaviour if guardrails are weak.
- Integration complexity – legacy systems increase deployment time.
- Unrealistic ROI expectations – CFOs often underestimate change management costs.
Outlook: Next 3–6 Months (Time-Bound)
Expect enterprises to accelerate:
- Deployment of 3–10 AI agents per business unit
- Adoption of process intelligence + agent orchestration
- Movement toward policy-aligned agents with trackable reasoning
- Increased focus on cost-to-serve metrics in automation reporting
Where adoption will be fastest
Finance, procurement, healthcare administration, logistics, and customer operations.
Direct Answers to Executive Questions
How much does business process automation cost?
Between $30k and $250k per workflow, depending on complexity, integrations, and AI involvement.
Which processes should be automated first?
High-volume, rules-based workflows with clear inputs/outputs: invoicing, approvals, customer service triage, HR onboarding.
How long does ROI take?
3–12 months depending on automation type (RPA is fastest, hyperautomation is longest).
What are the main risks?
Process fragmentation, governance gaps, poor data quality, and integration failures.
Which industries see the highest ROI?
Financial services, healthcare administration, logistics, retail operations, and shared services.
Glossary Box (Key Terms)
BPA: Automation of business workflows
RPA: Rule-based task automation
IA: Automation + AI for semi-structured decisions
Hyperautomation: Integrated automation ecosystem
BPM: Business process analysis and optimization
AI Agent: Software entity that performs multi-step tasks autonomously
Process Mining: Data-driven analysis of process execution
Low-code/No-code: Platforms for rapid application creation
Conclusion
BPA—and especially AI agent development—is shifting from experimentation to enterprise infrastructure. Costs remain variable, but ROI windows are tightening as orchestration frameworks mature and compliance requirements intensify. The next six months will emphasize scalable agent ecosystems, governance, and cost-to-serve optimisation, defining automation strategy across global enterprises.

#AIAgentDevelopment #BusinessProcessAutomation #IntelligentAutomation #Hyperautomation #WorkflowAutomation #RoboticProcessAutomation #DigitalTransformation #EnterpriseAutomation #AIinBusiness #AutomationStrategy #OperationalEfficiency #ProcessIntelligence #CostReduction #AIROI #FutureOfOperations #AutomationTools #Vsurgemedia
